Explore
Inverse Relations and Functions Solutions
Note
In other words, the domain contains a unique set of values.
Functions were introduced in Algebra 1: Principles of Secondary Mathematics. This lesson continues to grow this knowledge.
Note
The notation is read “a and b are elements of the set complex numbers.”
The phrase “if and only if” in mathematics tells you that the statement is true forward and backward.
In mathematics, there are often exceptions to rules. Therefore, take special note when you encounter words like “every,” “always,” and “must.” These words mean there are no exceptions to the rule.
Example 1
Represent relation R as a table. Represent the inverse of the relation as a mapping.
R
| x Domain |
y Range |
| –2 | –3 |
| 0 | 2 |
| 1 | –1 |
| 3 | –5 |
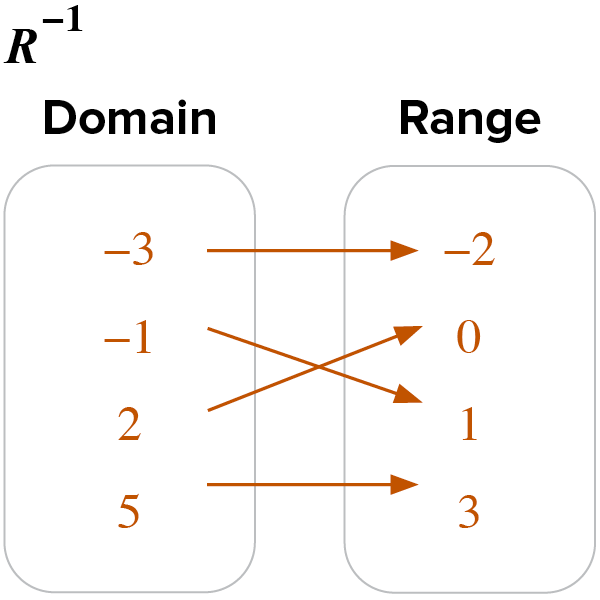
Note
Recall that when mapping, write the domain and range values in numerical order.
Compare the domain and range of R and Explain if either R or are functions.
The domain of R is the range of and the range of R is .
because each domain is unique.
Example 2
A small town surveyed its community to determine the type of transportation townspeople use in a typical week. The survey collected the type of transportation people used and the number of wheels associated with the transportation. A relation was written to compile the data.
Find the inverse of the relation. Explain how you know if the relation and its inverse are functions or not.
W = {(bicycle, 2), (car, 4), (truck, 4), (semi-truck cab, 10), (motorcycle, 2), (feet, 0), (SUV, 4)}
domain: {0, 2, 4, 10}
range: {bicycle, car, feet, motorcycle, semi-truck, SUV, truck}
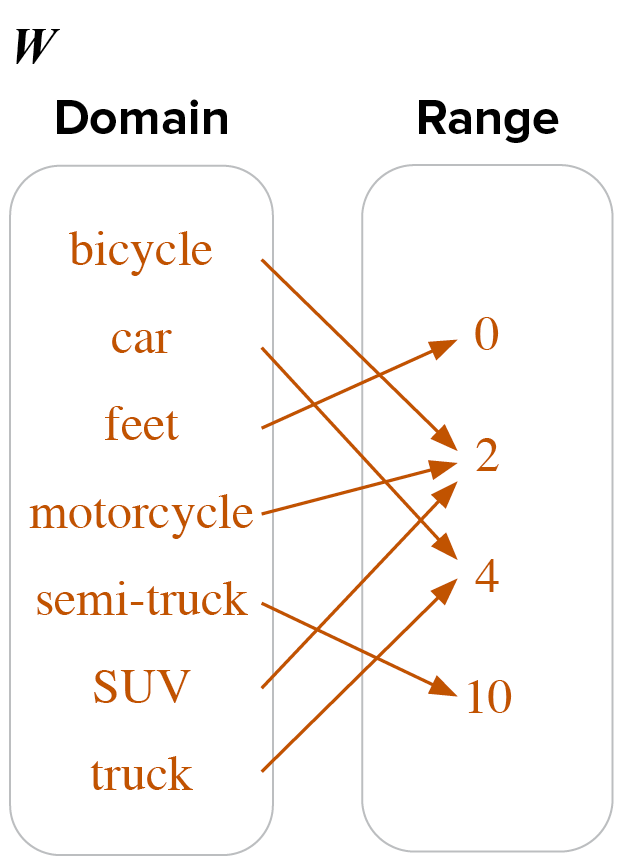
The relation W is a function because each type of transportation, or the domain, is unique .
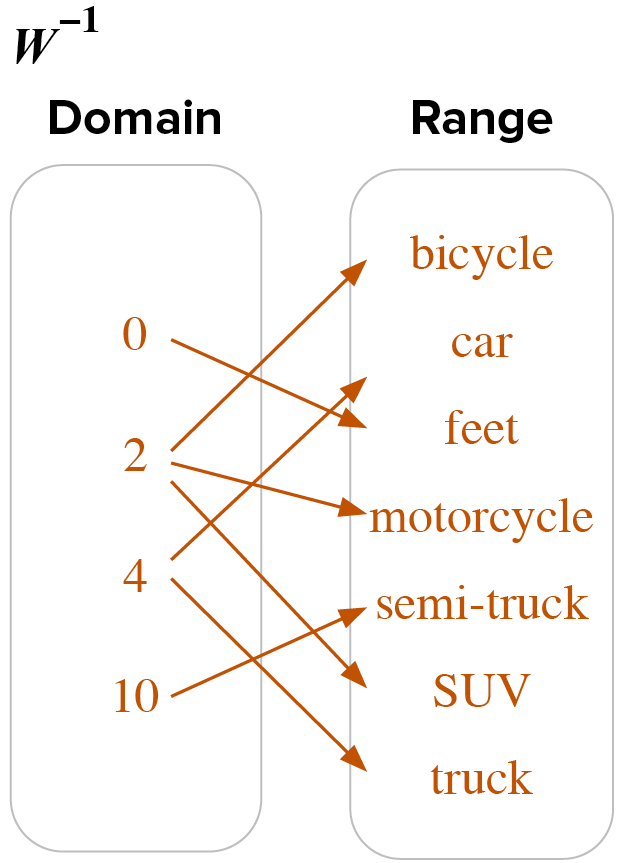
is not a function because multiple types of transportation have the same number of wheels, which means the domain has repeated values.
