Explore
Solving Square Root Inequalities Solutions
Note
Naming the restrictions for the radicand is also a step in graphing square roots and finding the domain, which will be covered later in this level.
Example 1
Solve. Graph the solution on a number line.
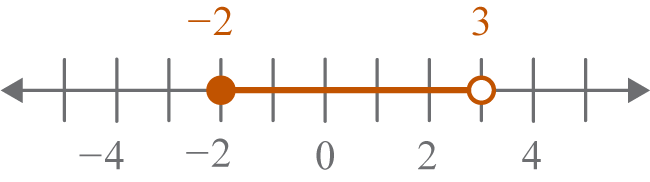
Implement
Restrictions
Solve
Explain
- All values must be greater than or equal to – 2 so that the principal root is true
- Isolate the radical expression
- Square both sides
- Solve for x
- Use the restriction on the radicand and the answer to the given problem to determine all solutions
Note
Use mental math to check values ≥ 2, between – 2 and 3, and < 3 to confirm answers.
Using a calculator to check can be helpful so that decimal values can be compared rather than fractions with uncommon denominators.
Example 2
Solve. Graph the solution on a number line.

Implement
Restrictions
Explain
- The restriction should be true for both radicand inequalities.
Solve
No solution
x cannot be greater than 1 and less than at the same time.
Example 3
Solve. Graph the solution on a number line.
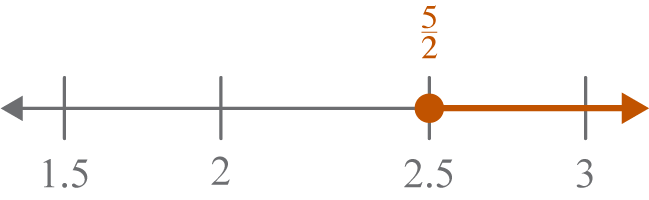
Restrictions
What if the inequality was ≤ ?
Solve
The principal root will always be greater than a negative number.
Note
The restriction for the radicand is the solution.
Note
The principal square root is positive and a positive number cannot be less than or equal to a negative number.
Example 4
Solve. Graph the solution on a number line.
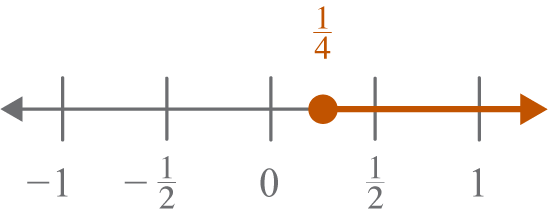
Restrictions
Check
Solve
Note
Use because this produces the most restrictive answer.
