Lesson 1: Practice 1 Solutions
- Simplify the fractions below. Then convert each fraction to a decimal.
| Simplified Fraction | Decimal | ||
| 0.40 | |||
| 0.20 | |||
| 0.60 | |||
| 3.0 |
List each vocabulary word beside its description.
Word Bank
Real Numbers
Whole Numbers
Rational Numbers
Natural Numbers
Integers
Irrational Numbers
- Decimals that do not repeat or terminate. Irrational numbers
- All existing numbers, not fictional numbers or terms. Real numbers
- Positive whole numbers, starting with 1, that are used in counting. Natural numbers
- Positive and negative whole numbers, as well as fractions that simplify to a positive or negative whole number. Integers
- Positive numbers beginning with 0. Whole numbers
- Positive and negative numbers, including fractions that simplify to terminating or repeating decimals. Rational numbers
- Complete the table below by coloring in or marking each category the number fits into.
| Irrational Numbers | Real Numbers | Rational Numbers | Integer | Whole Numbers | Natural Numbers | |
| X | X | X | ||||
| 0.93103448275… | X | X | ||||
| 3.910472… | X | X | ||||
| X | X |
- Construct a number line and plot each of the values below.
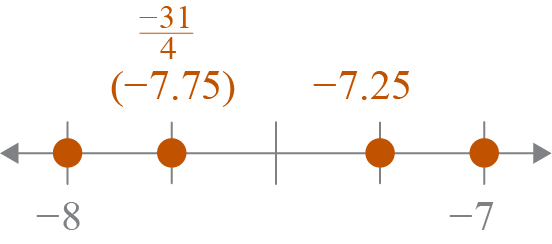
- Is the value rational or irrational? Provide evidence to support your answer.
The value is a rational number because irrational numbers can not be recorded as fractions. To further prove that the value is rational, simplify the fraction to a whole number.
Proof:
